ITIC 2021 Global Server Hardware, Server OS Reliability Survey Results
The technical and business challenges posed by the ongoing global pandemic didn’t compromise the core reliability of IBM, Lenovo, Huawei, Hewlett-Packard Enterprise and Cisco servers.
For the 13th straight year, IBM’s Z mainframe and mission critical Power servers achieved the highest server hardware reliability and delivered the strongest server security, among 15 different platforms, in ITIC’s annual 2021 Global Server Hardware, Server OS Reliability Survey.
And for the eighth consecutive year, Lenovo’s ThinkSystem servers again matched their best recorded uptime among all Intel x 86 servers along with Huawei’s KunLun and Fusion platforms. The HPE Superdome and the Cisco UCS hardware (in that order), rounded out the top five most reliable vendor hardware platforms (See Exhibit 1).
ITIC’s 2021 Global Server Hardware, Server OS Reliability independent Web-based survey, polled 1,200 corporations across 28 vertical market segments worldwide on the reliability, performance and security of the most popular server platforms from January through June 2021. Additionally, the preliminary findings from ITIC’s 2021 Global Reliability updated survey conducted from September through November 2021, indicate that the IBM Z, IBM Power servers; the Lenovo ThinkSystem and Huawei KunLun and Fusion servers continue to dominate and deliver the highest uptime, availability and security in datacenters and the cloud.
Among the top survey findings:
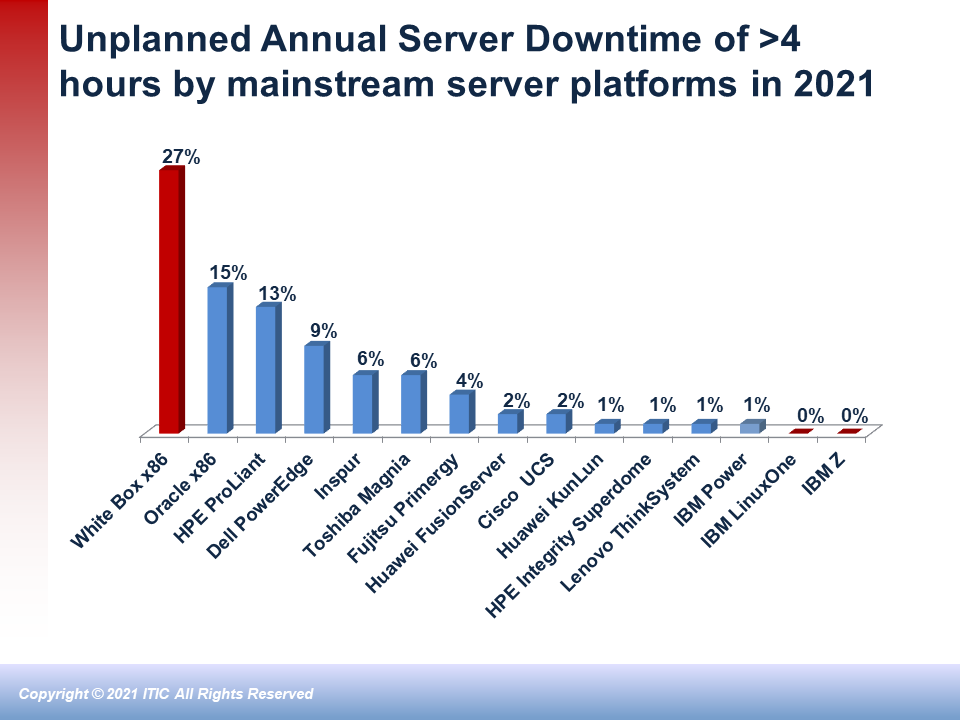
- Server Reliability: IBM z14 and z15 outpaced all rivals, matching its best ever results: just 0.60 seconds of per server monthly unplanned downtime. The IBM Power models also equaled their best uptime scores over the last 13 years, with just 1.49 minutes of unplanned per server downtime. The Lenovo ThinkSystem and Huawei KunLun platforms followed closely, each with 1.51 minutes of unplanned per server outages. Inspur was in the middle of the pack with 11 minutes of unplanned per server downtime, while the Dell PowerEdge servers posted 26 minutes of unanticipated outages. Unbranded White box servers (which often run unlicensed or pirated software) again were the least reliable servers with 57 minutes of unplanned per server downtime; this is up two (2) minutes from 2020.
- Server Availability: The IBM Z servers are in a class by themselves, a 94% majority of IBM Z customers said their businesses achieved unparalleled fault tolerant levels of six and seven nines – 99.9999% and 99.99999% reliability and continuous availability, the best among all server distributions. The IBM Power is close behind with 91% of customers reporting that the Power9 and latest Power10 models deliver a minimum of five and six nines availability/uptime. Meanwhile, 90% of Lenovo ThinkSystem, Huawei KunLun and HPE Superdome enterprises said their businesses achieve a minimum of five and six nines server availability.
- Cost Effectiveness/Total Cost of Ownership: The most reliable IBM z14 and z15; IBM LinuxONE III and the PowerPower8 and PowerPower9 servers deliver the best TCO and near immediate Return on Investment (ROI). A single minute of per server unplanned downtime on an IBM z14 or z15 server, calculated at a rate of $100,000, costs enterprise customers $1,002. One minute of unplanned downtime on a single IBM Power8 and Power9 calculated at $100,000 an hour costs $2,488. The upcoming Power10, slated to ship in September will likely offer better reliability and lower costs even further. The Lenovo ThinkSystem and Huawei KunLun and Fusion offerings each averaged 1.51 minutes of unplanned per server outages; that equates to per server/per minute downtime charges of $2,521. Unbranded White box servers with 57 minutes of unplanned per server downtime could cost corporations $95,190 when hourly downtime losses are calculated at $100,000 (See Exhibit 3 and Exhibit 4).
- Security hacks, user error and remote working/remote learning are the top three causes of unplanned downtime. A 73% majority of survey participants cited security as the number one cause of unplanned server downtime; 64% said human error caused unplanned server outages. Meanwhile, 58% of survey participants attributed increased downtime to management and security issues related to COVID-19 issues like remote working and remote academic learning via Zoom meetings for K-through-12 and college classes. While offices and schools were closed during the global pandemic during 2020 and much of 2021, IT and security administrators were hard pressed to effectively manage and secure remote PCs, laptops, notebooks and tablets. Consequently many employees and students did not adequately secure their personal devices. An April 2021 Fortune magazine article noted that hybrid and remote workplace and academic environments created many positive opportunities for businesses and schools, but they also represent a potential boon for hackers.
In 2020, cybercriminals transmitted 61% of malware through cloud applications to target remote workers, according to the July 2021 Netskope Cloud and Threat Report . The report said that utilizing cloud-based applications enables hackers to circumvent older, legacy Email and Web-based security solutions. The Netskope report further noted that security risks are exacerbated by the fact that 83% of employees and students access sensitive personal data via applications installed on corporate and academic devices e.g., laptops, notebooks and tablets. This can result in dire consequences in the connected digital era. To cite one example, in March 2020, the California State Controller’s Office, which handles $100 billion a year, suffered an email phishing attack on an employee that enabled cyber criminals cloud access to internal documents; once they gained entrance to the employee’s device they were able to successfully phish another 9,000 employees.
The reliability and security of server hardware, server operating systems and mission critical applications are critical elements of the core datacenter, network edge and cloud infrastructure.
Eighty-nine (89%) percent of organizations require a minimum of “four nines” – 99.99% reliability to ensure uninterrupted daily business operations and secure data assets to sustain the company’s revenue stream and mitigate risk. And over one-third of organizations now strive for “five nines” 99.999% of uptime; this equals 5.25 minutes of per server unplanned downtime.
Each second and minute of server downtime and the associated mission critical applications costs the business money and raises transactional operations and monetary risks.
In the digital era of interconnected intelligent systems and networks, unplanned downtime of even a few minutes is expensive and disruptive and can reverberate across the entire ecosystem. This includes datacenters; virtualized public, private and hybrid clouds; remote work and learning environments and the intelligent network edge.
ITIC’s 2021 Hourly Cost of Downtime survey indicates a single hour of server downtime totals $300,000 or more for 91% percent of mid-sized enterprises (SMEs) and large enterprises. And among that 91% majority – nearly half or 44% – of corporations said, hourly outage costs exceed one million ($1M) to over five million ($5M).
ITIC 2021 Global Server Hardware, Server OS Reliability Survey Results Read More »